Types of Thyroid Cancer Treatments
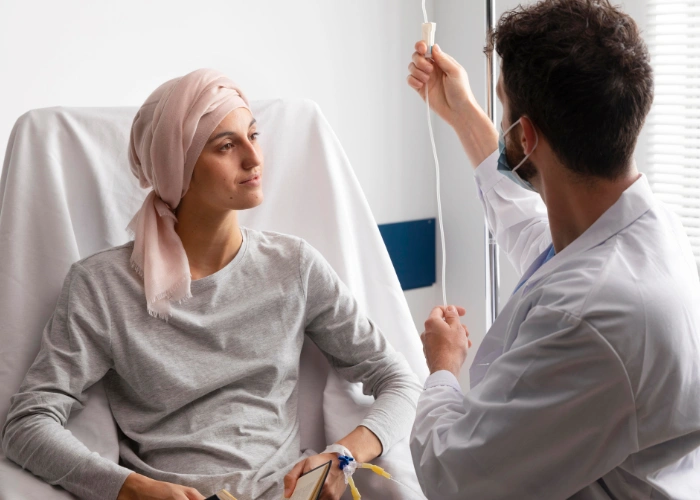
Surgery - The primary treatment involves removing part (lobectomy) or all (total thyroidectomy) of the thyroid gland. Lymph node dissection may be required if cancer has spread.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy (RAI) - RAI uses radioactive iodine to destroy remaining cancer cells after surgery. It is most effective for papillary and follicular thyroid cancer but unsuitable for pregnant women.
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) - High-energy radiation targets and kills cancer cells, mainly for anaplastic thyroid cancer or cases where surgery is not an option. It is often combined with chemotherapy for better results.
Targeted Therapy - Drugs that target specific genes or proteins involved in cancer growth, like PARP inhibitors.
Hormone Therapy (Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy) - Patients need levothyroxine (T4 hormone) after surgery to replace lost thyroid function and suppress TSH, which could trigger cancer regrowth.
Targeted Therapy - Drugs like Lenvatinib and Sorafenib block cancer cell growth by targeting specific genetic mutations. It is mainly used for medullary and advanced thyroid cancer that does not respond to RAI.
Chemotherapy - Anti-cancer drugs, such as Doxorubicin, kill rapidly growing cancer cells and are mainly used for anaplastic thyroid cancer. It is often combined with radiation therapy.
Immunotherapy - Boosts the immune system to fight cancer, particularly for advanced thyroid cancer with specific genetic markers. Drugs like Pembrolizumab are used in clinical trials.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis starts with a physical exam to check for lumps in the neck, followed by a thyroid function test and blood tests to measure hormone levels. Imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI help assess the tumor. A fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy confirms the diagnosis and determines cancer type and stage.
Diagnostic Cost in India
| Diagnostic Procedure |
Cost in USD |
| Blood Tests |
50 to 80 |
| Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) |
100 to 150 |
| Ultrasound Imaging |
30 to 50 |
| Thyroid Scan (Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test) |
100 to 150 |
| CT Scan/MRI/PET Scan |
500 to 800 |
Surgery Cost in Indian Cities
| City |
Cost in USD |
| New Delhi / NCR |
3000 to 9500 |
| Mumbai |
5500 to 10500 |
| Bangalore |
4500 to 10000 |
| Chennai |
3500 to 10000 |
Surgery Cost Inclusions
| Pricing Inclusions |
Option |
| Routine patient investigations before surgery |
Included |
| First Consultation |
Included |
| Type of treatment advised |
Included |
| Surgeon fee, OT charges, anesthesia |
Included |
| Routine drugs and consumables required during hospitalization |
Included |
| Pre-anesthesia check up and clearance |
Included |
Top Hospitals in India for this Surgery
- Artemis Hospitals, Gurgaon
- Max Hospital Gurugram
- Gleneagles Global HealthCity, Chennai
- Max Super Speciality Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon
- Medanta - The Medicity, Gurugram
Factors Affecting Thyroid Cancer Treatment in India
Please note that the costs mentioned above are only indicative and not conclusive, as multiple factors influence the final cost of your treatment journey. These factors include:
Age of the patient; the choice of location, doctor and hospital; type, size and location of the tumor; stage and grade of cancer; pre-existing medical history; type and duration of treatment advised; type of approach drug used; type of surgery approach; need for extended hospital stay; need for any other additional treatment; type of surgery and approach; overall patient status and condition at the time of surgery; hotel stay, meals, and flights; extended hospital stay; post-operative follow-ups and medical management; post-operative dressing and nurse visits; any required blood products; complications management; treatment for any other underlying medical conditions; and any complex investigations.